Charging an electric vehicle (EV) is a bit more complicated than with an internal combustion engine vehicle (ICEV). With ICEVs, it doesn’t matter which gas station you pull up to, all the nozzles will fit your vehicle and will refuel the tank within five minutes.
There may be different blends of gas and a separate diesel nozzle, however every pump accommodates each of these options.
On the other hand, charging an EV is slightly more nuanced. Instead, there are three levels of EV charging. Each of these levels provide different amounts of power, have different locations, and even have different plugs.
At first, this may seem way to overcomplicated than gas. However, after a bit of time, it will become second nature. Think of this as the transition from a regular cell phone to a smartphone. Smartphones have apps, software updates, and WiFi connectivity that required a bit of a learning curve.
After a while, people got used to them as the overall benefit of a smartphone outweighed the regular cell phone. The same goes for EVs.
This article will breakdown the three levels of EV charging to clarify any questions or doubts for the first time electric car shoppers out there. Let’s get started!
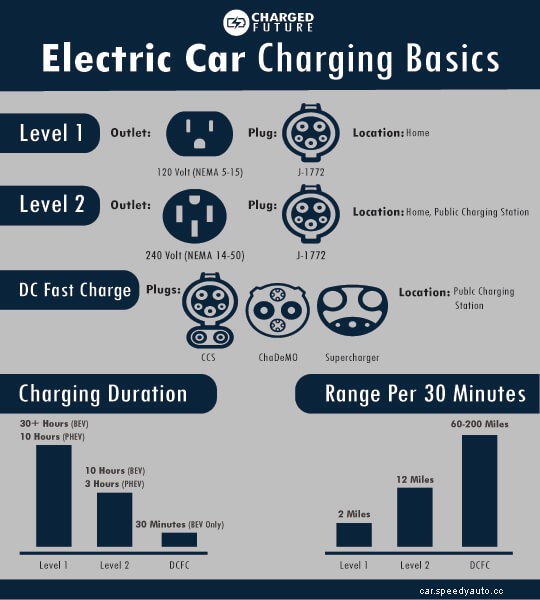
Level 1 charging, also known as “trickle charging”, utilizes a regular 120V outlet. As such, charging is quite slow. In fact, Level 1 charging only provides around 4 miles of range per hour.
For plug-in hybrid electric vehicles, or PHEVs, this can be a good solution since the batteries are much smaller than a battery-electric vehicle, or BEV. PHEVs can completely recharge in around 12 hours on Level 1 charging.
For BEVs, it is a different story. BEVs can take days to charge on Level 1–ergo trickle charging.
Lastly, Level 1 charging is typically only at home.
Level 2 charging is the next step in EV charging. Through a 208/240V outlet, Level 2 charging provides around 25 miles of range per hour.
Level 2 charging can recharge a PHEV in around 3 hours and a BEV in around 8 hours. As such, Level 2 charging is the preferred method for home charging.
Home EV chargers cost around $300 to $700. Popular brands include Enel X, Chargepoint, Clipper Creek, Grizzl-E, and Blink.
Additionally, Level 2 chargers are also found at workplace and public charging stations. Use the Plugshare map below to find nearby Level 2 public charging stations.
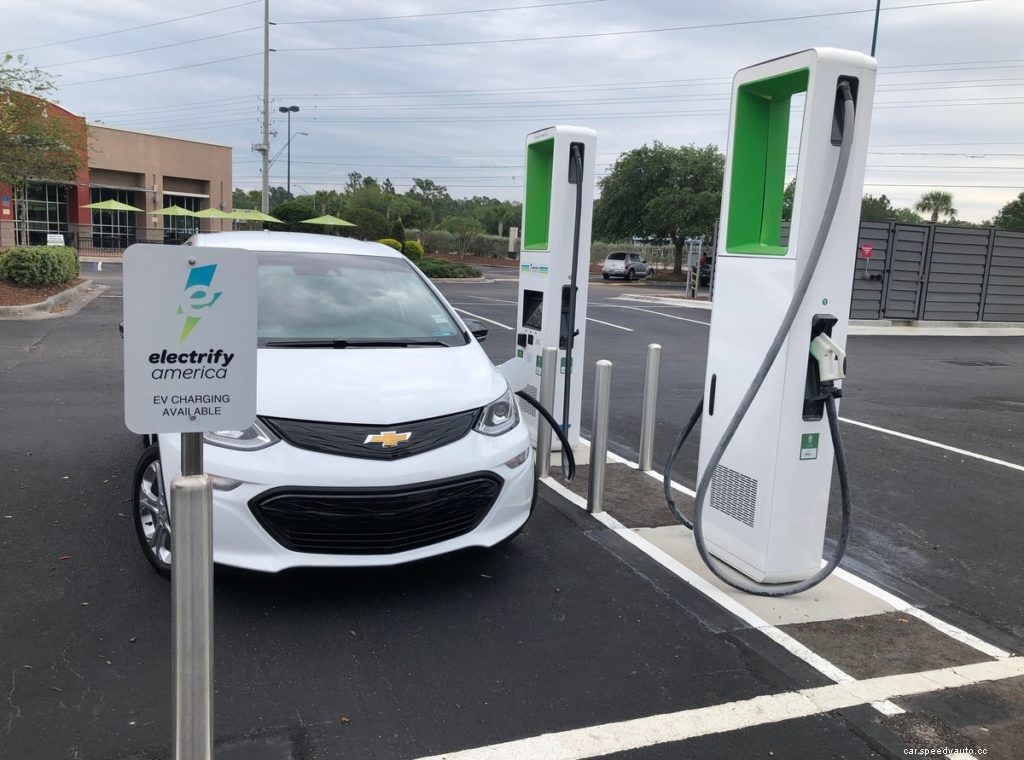
The third and final level of charging is Level 3. More commonly known as DC Fast Charging, or DCFC, Level 3 charging is the fastest way to charge an electric car.
At over 400V, DCFC can recharge a BEV in around 30 minutes. PHEVs are typically not capable of DCFC since they have a gas back up.
With the very high voltage, DC Fast Charging is only found at public charging stations. Use the Plugshare map below to find nearby DCFC stations.
As you can see, there are many DCFC stations throughout the United States and Canada. This is because of extensive nationwide charging networks such as Tesla, Electrify America, EVgo, and Chargepoint.
As of 2020, there are over 28,000 public charging stations with over 94,000 ports per the Alternative Fuels Data Network.
