Dan Ferrell writes about do-it-yourself car maintenance and repair. He has certifications in automation and control technology.

A weak spark, or no-spark, problem may originate within one or more common ignition system components:
Other symptoms that may point to a weak spark plug include:
However, these symptoms are not necessarily caused by a weak spark plug; you may be dealing instead with a fuel system issue or poor compression in one or more cylinders. So you need to determine, before you do any work, whether you have a weak spark or no spark.
The next sections will help you determine a weak spark and potential problems affecting ignition spark.
It is recommended to have on hand the vehicle repair manual for your particular vehicle make and model. If you don't have this manual yet, you can buy a relatively inexpensive copy through Amazon. Haynes manuals include step-by-step procedures, images, and electrical diagrams for diagnostics, maintenance jobs, troubleshooting tasks, and parts replacement projects. So you can recoup your investment in a short time.
| Index |
|---|
1. How to Do a Quick Ignition System Check |
2. How to Check for Spark, Voltage Leaks and Resistance |
3. How to Interpret Diagnostic Trouble Codes |
4. How to Read Spark Plugs |
5. How to Deal With a Weak Spark |
6. Resources |

If you have noticed a mild problem with misfires or a no-start condition, but the engine still cranks, this quick test (for vehicles with a crankshaft position sensor) can lead you to the source of the problem:
When cranking or starting the engine:
If the tachometer doesn't work or seems unstable (engine misses), check the ignition system primary circuit:
If the tachometer seems stable, check the ignition system secondary circuit:
Consult your vehicle repair manual to verify the configuration of your particular ignition system and components. Also, refer to the Resources section at the bottom of this post for more help.

Diagnosing spark, leaks and resistance are common tests you can do when dealing with ignition system problems. These tests are closely linked to ignition system basic maintenance procedures.
If possible, use an adjustable spark tester for this test.
The spark on the tester should be a bluish-white color; an orange or red color indicates a weak spark.
If you have a weak spark, you may be dealing with a:
depending on your ignition system configuration. Consult your vehicle repair manual.
The following video shows you how to use a spark tester.
Spark plug wires wear out after years of operating under extreme temperatures (hot, cold), engine vibration, and contamination from oil, grease and coolant.
The wire can leak voltage or increase resistance (on carbon-core wires) and interfere with ignition coil voltage.
Check your spark plug wires for visual damage like cuts, chafing, and breaks that might leak voltage to ground.
Quick test for leaking ignition voltage:
Spark plug wire resistance check:
The typical lifespan of a spark plug wire is around 50,000 miles. That's when internal resistance (carbon-core wires) begins to increase.
You can use an Ohmmeter to check your spark plug wires' resistance.
Most plug wires will have a resistance of 12,000 Ohms per foot. Consult your vehicle repair manual.
If you need help checking your spark plug wires, head over to the "Resources" section at the bottom of this post.
If the test light blinks at any point, that wire is leaking voltage.
One of the first checks you want to do early in your diagnostic procedure is to download potential trouble codes (DTCs) from your computer memory.

One of the first checks you want to do early in your diagnostic procedure is to download potential trouble codes (DTCs) from your computer memory. You want to do this whether the check engine light (CEL) is on or not. Often, a pending code can give you a clue to the problem. If you don't have a scanner, your local auto parts store can download trouble codes for you.
P0300 misfire code series:
A specific code like P0301, which signals a misfire on cylinder one, may point to a:
If necessary, check the spark plug chart in your vehicle repair manual to read for spark plug potential problems.
If there are no other codes present besides a P030(0+) code:
You may be dealing with an ignition issue or fuel system issue. Check for:
However, keep in mind that a weak coil, injector, or dirty injector may not trigger a CEL.
Other DTCs Present:
If you find a misfire code along with a fuel injector or ignition coil related code, check the fuel injector first.
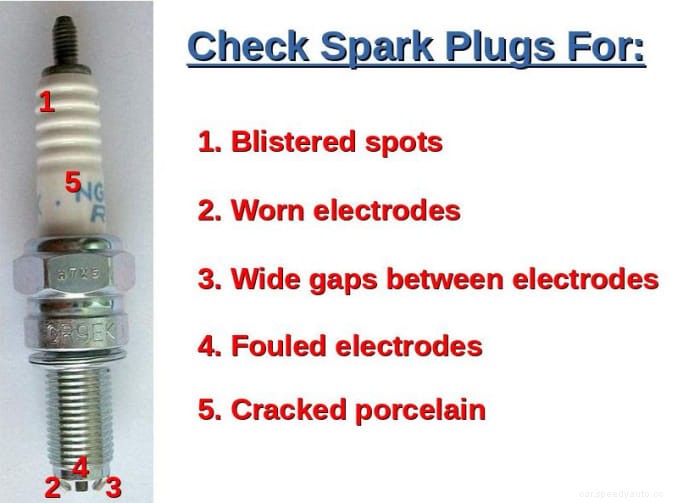
Removing and inspecting spark plugs can give important clues about what type of problem, if any, is affecting your engine and what to do about it.
Check the spark plug chart included in your vehicle repair manual.
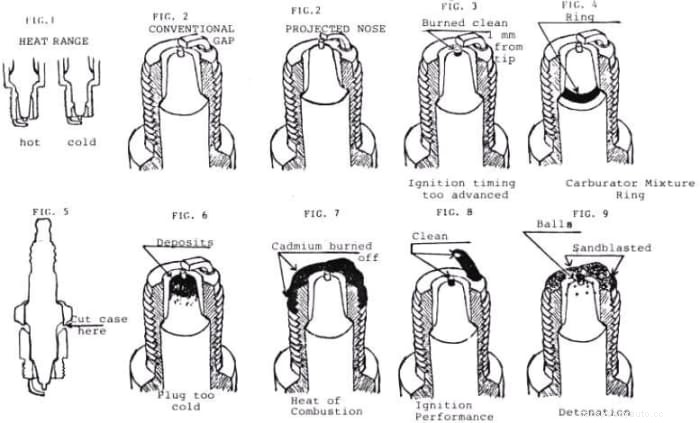

Dealing with a weak spark in one cylinder is usually not too difficult to diagnose. However, a random weak spark that results in random misfires is another story.
Either condition may cause damage to components and result in expensive repairs if not fixed on time.
An electrical "open" or low resistance in a coil primary circuit can lead to:
An electrical short in the primary circuit can lead to:
An electrical "open" or high resistance in the secondary circuit can lead to:
An electrical short or low resistance in the secondary circuit can lead to:
Weak sparks allow unburned or partially burned fuel to flow into the exhaust system. Eventually, this will damage other components like the oxygen sensor, catalytic converter, and EGR system (through excessive carbon buildup).
This article is accurate and true to the best of the author’s knowledge. Content is for informational or entertainment purposes only and does not substitute for personal counsel or professional advice in business, financial, legal, or technical matters.